In this article, we will have a basic introduction to operating systems and virtualization to help you get started with Linux for DevOps. Let's start with a basic question, what is the first thing that happens when you start your computer -
The answer is - it executes softwares that are there in the BIOS. A BIOS is a basic input output system, also referred to as firmware. This firmware comes by default in the computer and is stored in a small chip that is there in the motherboard.
The reason to do that is to make sure that the system is working correctly or not. It will make various checks like -
- If the RAM is there or not
- What devices are connected to the system
- what drives are there, etc
All these checks are being made to identify if the system is ready to launch the Operating System or not.
Once, the Operating system is launched. It will load the bootloader but this might not be the case all the time, it depends on different scenarios but in most cases, a bootloader is responsible to initialize the operating system. Different Operating Systems might have different bootloaders that come with them.
So, that is what happens when we start a computer.
Now let's talk about what is an operating System -
In simple terms - An operating system is a software to manage and operate a computing device. These computing devices can be anything like a smartphone, tablet, laptop, etc.
For any software to be considered as an operating system, it needs a Kernel, File System, and User Interface - it could be CLI or GUI, also should be able to take and manipulate data based on commands.
Now, let's talk a little bit about kernel and File Systems -
What is a kernel?
It is the core of any operating system and it generally has complete control over everything in the operating system. It is responsible for the interaction between software & hardware and that is the main reason it has complete control over the system.
What is a file System?
It is a method or a data structure that the Operating system uses to store and retrieve data in the memory. Now that we know what an operating system is, let's learn what are some of the major operating systems out there -
- Windows
- Mac OS
- Linux
These three Operating Systems are the most famous ones, but our focus is going to be on Linux -
You may ask, why Linux over the other two? Let's see -
Before that, The very first thing we must know is that Mac OS and Linux are pretty similar as they both are UNIX based. However, Windows, on the other hand, has some components that are UNIX based but, majorly it has been derived from other operating Systems.
Why use Linux?
As a DevOps Engineer, you will have to automate certain tasks. To do this, you will need to write some small scripts. This can be done either with Bash scripting, python, or golang.
Another reason is that most containers are configured to run only on a Linux Environment. Containers are isolated environments where one can run applications.
Also, a lot of tools that make a DevOps Engineer's life easier, run on Linux.
Let's also talk a little bit about the history of Linux -
History of Linux
In 1969, there were two developers, one was Ken Thompson and the other one was Dennis Ritchie. These two developers were working for bell laboratories and while working there, they came up with the first UNIX operating system.
later on, after some time, they rewrote the entire operating system in C language and it was majorly to make the operating system more portable and soon it became a widely used OS around the world.
A decade later a programmer named Richard Stallman started working on the GNU project. In 1991, Linus Torvalds started working on something which we now know as the Linux Kernel. This Linux kernel is the unified Linux kernel which is used by all distributions out there in today's time.
Now there are a lot of Linux Distributions, which one to choose?
In my opinion, As a beginner, the focus should not be on choosing the best OS distribution but on learning as later on, one can switch to any Distribution they want. So, I'll be going on with Ubuntu. You can choose any distribution of your choice.
Now, Before getting started with Basic commands of Linux. Learning about virtualization and virtual machines is important.
Virtualization
Virtualization is a process that allows more efficient utilization of physical computer hardware. It uses software to create a layer over computer hardware that allows, the computer hardware(processors, memory, storage, and more) to be divided into multiple virtual computers, commonly known as virtual machines(VMs). Each VM runs its own operating system(OS) and behaves like an independent computer, even though it is running just on a portion of the actual underlying computer hardware.
Virtual Machine
A virtual machine is a virtual representation of a physical computer. They are often referred to as a guest while the physical machine they run on is referred to as a host. A VM cannot interact directly with a physical computer. Instead, it needs a lightweight software layer called a hypervisor to coordinate between it and the underlying physical hardware. The hypervisor allocates physical computing resources.
How Virtualization works
When a hypervisor is used on a physical computer or server, it allows the physical computer to separate its operating system and applications from its hardware.
Then, it can divide itself into several independent virtual machines.
Each of these virtual machines can then run its own operating systems and applications independently while still sharing the original resources(RAM, storage, etc) with the physical computer(also known as a bare metal server), which the hypervisor manages.
There are primarily two types of hypervisors -
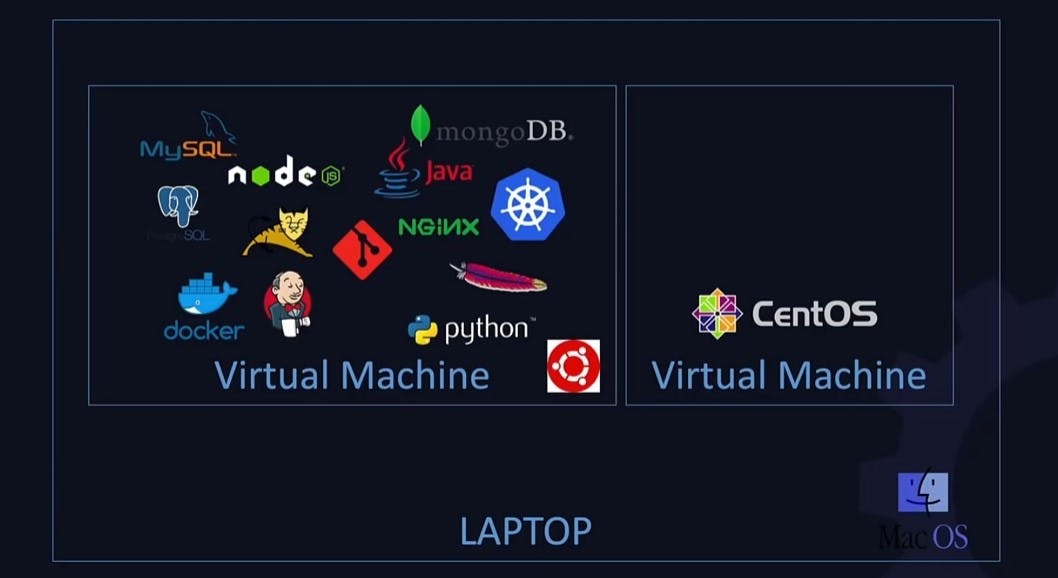
Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware(usually a server), and then the VMs are created on that. Examples - VMWare ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-v. Now, these are used in enterprises and production environments where one needs to create and manage large no. of virtual machines and also these hypervisors have large resource requirements. They also need to be installed and configured directly on the laptop and they are expensive as well.
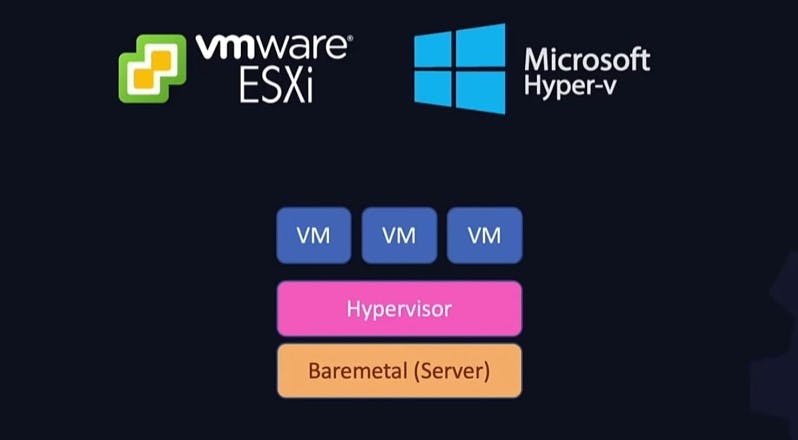
A lot of people do use these for home labs especially if they have systems with high resources but that is not what we want to do, for our purpose there are other solutions that better suit our needs and are easily available and they are called type-2 hypervisors.
Type 2 hypervisors run as an application within a host OS and usually target single-user desktops. We can manually create a VM and then install a guest OS in it. Examples are Virtual Box and VMware workstations, these allow us to easily get started with the virtual machine on our laptop. Both of these are very easy to get started with, just download then install and you are good to go.

How to setup Lab Environment
To set up our own lab Envrovironment we have two options one on our personal computer, and the second on the cloud. For now, let's set up a lab environment on a personal computer.
But before that, you may ask why we even need to set up a lab environment -
While learning DevOps, we'll come across a set of tools that w'll be working with. We can install all of them directly on our laptop but at some point, it's going to start impacting the performance of our laptop and we might also run into compatibility-related issues.
So one thing to combat that is to do everything that we need to do within a virtual machine on our laptop and this way if things go south we can simply delete a virtual machine and provision a new one or take a backup of our virtual machine and restore state from a backup.
This also allows one to try different virtual machines and have different operating systems on different virtual machines, Irrespective of what OS we are on. We can have as many systems as we want, as long as we have sufficient hardware resources.
The software that we will use to create this virtual machine is going to be VMware workstation.
So, Let's learn how to set up a lab environment using VMware workstation to work on -
First of all, you will need to download an Ubuntu Image, Here is the link to download the same - ubuntu.com/download/desktop
And, Here is the link to download VMware workstation - vmware.com/in/products/workstation-player/w..
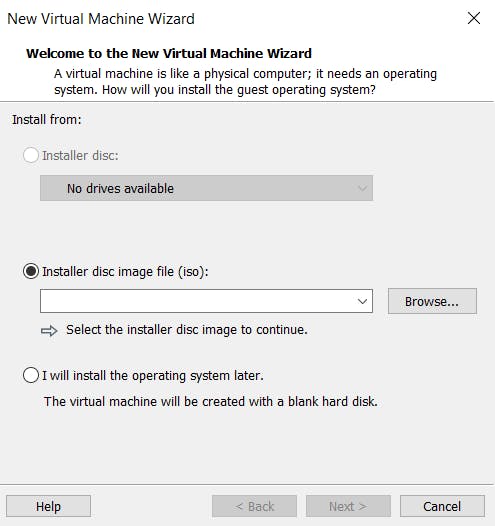
- Once it's installed open up the software. To create a new virtual machine click on the Create a New Virtual Machine.
- Click Browse to look for the ISO that you downloaded. Once you select it, click Open and then Next.
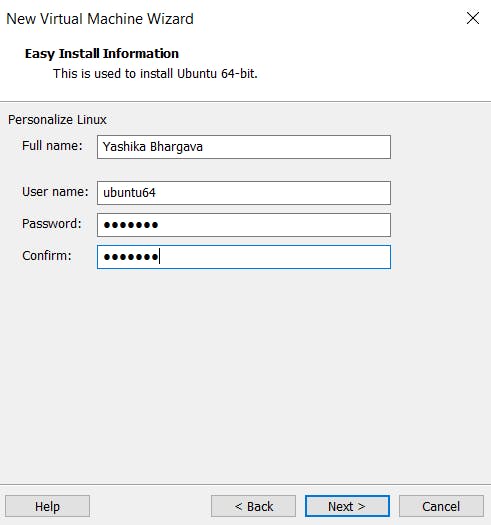
- Enter your full name, username, and password. Once you've done all that, click Next.
Then, specify the name of your virtual machine or leave it as default. Now, choose a location to store the virtual machine. Then click Next.
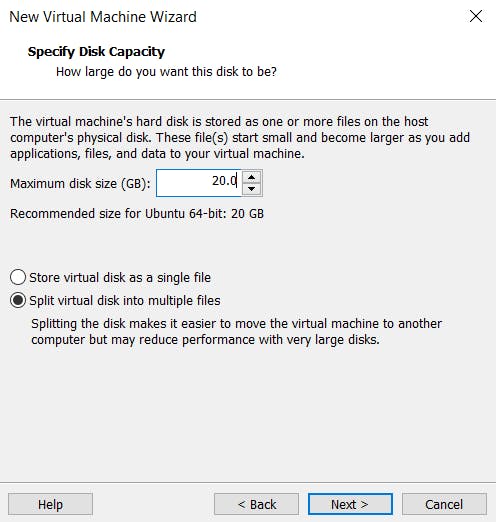
Enter the maximum disk size, for now, you can leave it as default and click Next.
Now, Click finish to create the virtual machine.
After that, the installation process should begin. If you are prompted to download VMware Tools, click Download, and Install.
After the installation process is done. Wait for the Ubuntu desktop to launch at the end of it, and then congratulations! You've successfully installed Ubuntu on VMware Workstation.
The next step for you from here will be to get started with Linux by learning basic Linux commands and that is all for now, Thank you for reading. I hope this article was helpful and you were able to take something out of it, your valuable feedback would be appreciated.